Reference
-
How to deploy a containerized spring boot application , with PostgreSQL as database on minikube.

-
This post will also share details on how to initialize the database with tables and data during the initialization process.
-
Will use a spring boot application order service with a REST endpoint to fetch customer details
GET /customers
-
It uses spring JPA to access PostgreSQL
-
Details of the service - https://github.com/rajeshsgr/order-svc-k8
-
This article will demonstrate deploying this service on Minikube , More details on minikube can be found at- https://belowthemalt.com/2022/03/17/minikube-kubectl-and-local-development-deployment-of-apps-in-kubernetes/
-
Key steps for this deployment process are
- Building a docker image of order-service & upload to docker repository
- Writing Kubernetes deployment file to initialize and run database
- Writing Kubernetes deployment file for order-svc
- Testing the service
Step 1: Building a docker image of order-service & uploading to docker repository
-
Build the application to generate jar file
mvn clean install -DskipTests
-
If you want to run this application is local , you will have to update the application.properties file with database details
-
Create a docker image for the service , refer to Dockerfile https://github.com/rajeshsgr/order-svc-k8/blob/main/Dockerfile
-
Dockerfile has mainly instructions to add openjdk 8 image, expose port 8080 and add the generated jar file from previous step to the image
-
To build an image with the name order-svc-k8 from the Dockerfile , run the below command
docker build -t raje/order-svc-k8 .
-
Once the above step is done you can check the image with docker images command
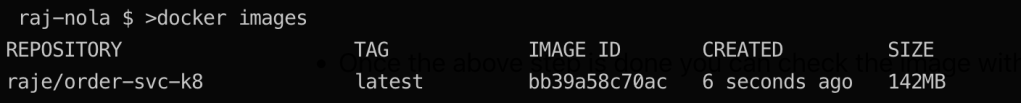
-
To push this image to docker repository, give the command
docker push raje/order-svc-k8
-
At this stage, we have built our spring boot app, dockerized it and uploaded to the docker repository
Step 2: Writing Kubernetes deployment file to initialize and run database
-
For PostgreSQL, we will use the docker image . Link to repo - https://hub.docker.com/_/postgres
-
Other 2 important use cases of this demo are
- Mount a path on host , so that the data can be retrieved even if the cluster goes down
- Initialize database with table and scripts
-
In order to mount a persistent storage, we will have to deploy a resource type of Persistent Volume and Persistent Volume Claim
-
Since we need a persistent storage for PostgreSQL to store data, we will provision the storage using Persistent Volume yaml
-
Above yaml is for PersistentVolume object , which has details of host path , storage class , size etc. The name defined for this is - postgresql-claim0
-
Persistent volumes have a lifecycle that is independent of any individual pod that uses the storage.
-
In order for our application to consume this storage space, we will have to request it using a Persistent Volume Claim request.
-
yaml for Persistent Volume Claim
-
Next we want to build a configuration map object, which will have our database initialization scripts
-
Configuration maps are kubernetes objects which are used to store non-confidential data in key-value pairs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: postgresql-initdb-config data: init.sql: | CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS customers ( customer_id bpchar NOT NULL, company_name character varying(40) NOT NULL, contact_name character varying(30), contact_title character varying(30), address character varying(60), city character varying(15), region character varying(15), postal_code character varying(10), country character varying(15), phone character varying(24), fax character varying(24) ); INSERT INTO customers VALUES ('ALFKI', 'Alfreds Futterkiste', 'Maria Anders', 'Sales Representative', 'Obere Str. 57', 'Berlin', NULL, '12209', 'Germany', '030-0074321', '030-0076545'); -
Since our order service will need to access this database, we will need a Kubernetes service object
-
Service is responsible for enabling network access to a set of pods
-
Services select Pods based on their labels. When a network request is made to the service, it selects all Pods in the cluster matching the service’s selector, chooses one of them, and forwards the network request to it.
-
Next, we need the deployment object.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: postgresql labels: app: postgresql tier: database spec: selector: matchLabels: app: postgresql strategy: type: Recreate template: metadata: labels: app: postgresql tier: database spec: containers: - name: postgresql image: postgres:12 imagePullPolicy: "IfNotPresent" env: - name: POSTGRES_DB value: northwind - name: POSTGRES_USER value: postgres - name: POSTGRES_PASSWORD value: changeme ports: - containerPort: 5432 name: postgresql volumeMounts: - name: postgresql-claim0 mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data - mountPath: /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d name: postgresql-initdb volumes: - name: postgresql-claim0 persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: postgresql-claim0 - name: postgresql-initdb configMap: name: postgresql-initdb-config -
Key elements of the deployment yaml
- Deploys postgres:12 container
- Have environment variables , which has the database name, user and password
- Mounts the persistent volume , defined using Persistent volume object
- Passes the configmap value for docker to execute
-
Bring minikube up by issuing command:
minikube start -
Let us now deploy all the kubernetes resources by giving following commands
-
You can check status by
kubectl get allcommand
-
In case you want to check the logs of database pod, you can check by issuing this command
kubectl logs pod/postgresql-7bf5994f6f-kv5gs. Please replace the pod name with your pod name -
Let us now verify this deployment , by connecting to database. Commands for the operations are -
kubectl exec -it pod/postgresql-7bf5994f6f-kv5gs bash -
Replace pod name with your pod name in the above command
-
Connect to postgres -
psql -U postgres -
Connect to northwind database -
\c northwind -
Check the tables -
\dt -
Check if database is initialized by executing -
select * from customers; -
The application.properties of the service , will get the details of database username, password and connection details from the environment variables mentioned in order service deployment yaml
1 2 3 4 5 6spring.datasource.username=${SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME} spring.datasource.password=${SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD} spring.datasource.url=${SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL} ]spring.jpa.show-sql=true spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update -
We will define a service object for us to access the application. yaml for service object
-
Service type is NodePort . It makes the service accessible on a static port on each Node in the cluster. This means that the service can handle requests that originate from outside the cluster.
-
Next is deployment of order service and the yaml for that is
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: order-svc spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: order-svc template: metadata: labels: app: order-svc spec: containers: - image: raje/order-svc-k8 name: order-svc ports: - containerPort: 8080 env: - name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD value: changeme - name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL value: jdbc:postgresql://postgresql:5432/northwind?useSSL=false - name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME value: postgres - name: SPRING_JPA_HIBERNATE_DDL_AUTO value: update -
Key elements of the deployment yaml
- uses - raje/order-svc-k8 container image
- Defines the enviornment variable
- database is accessed with the name postgresql which is the name of the service for database
-
Deploy the service and deployment objects by giving below command
-
You can verify the deployment with the command -
kubectl get all -
During the process if you want to check the logs of order service pod , you can give command
kubectl logs <<podname>> -
To access and test the application , issue the below command
1kubectl port-forward service/order-svc-service 7080:8080 -
To access the API
1curl http://localhost:7080/api/v1/customers
Source code for the application: https://github.com/rajeshsgr/order-svc-k8